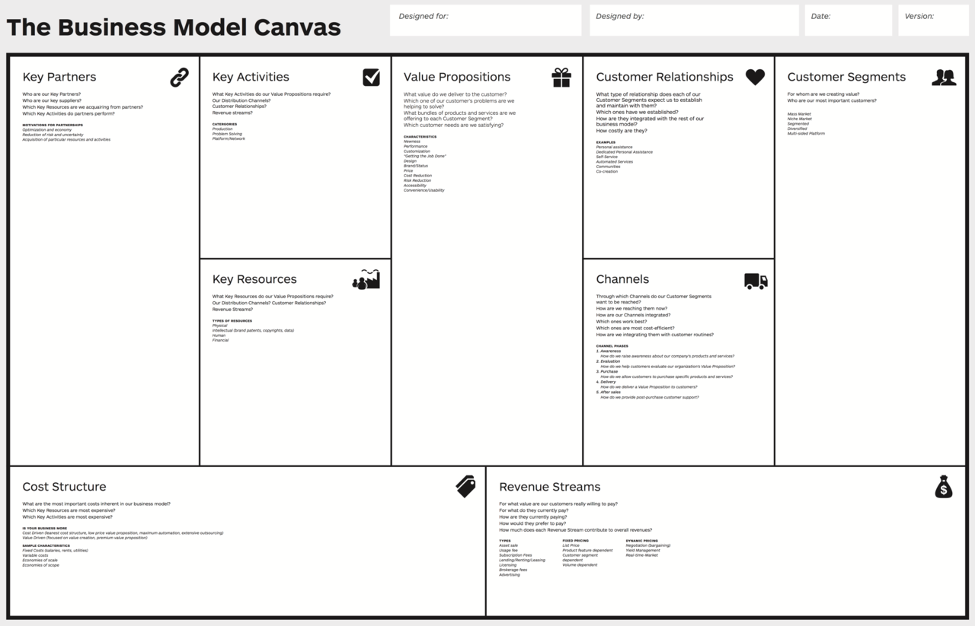
Business Model Canvas: Visualizing Your Business Model
The business model canvas is a strategic management tool that is used to visualize and assess your business or business idea. With it being a one page document it is much more effective and adaptable than a full multi-page business plan can be. I routinely leverage this to quickly get a comprehensive view of the business and get everyone on the same page as to what it is going to take to deliver the value proposition to the customer. Working through this process allows you to quickly identify the areas in which you have not fully thought through or that are a gap in your business.
The right side of the business model canvas focuses on the market or customer (external), while the left side focuses on the business (internal factors). In the middle of the external and internal factors is your value proposition.
Value Proposition
The value proposition is the core of what you offer to the market and as a result sits at the center of your business model canvas. It represents your unique solution or value creation for your customers.
Your value proposition should be clear, concise, and differentiate you from competitors.
Questions to ask yourself when defining your value proposition:
What problems are you solving for your customers or what needs are you fulfilling?
What value are you bringing to your customer?
What is the motivation behind this problem?
Customer Segments
Customer segmentation is about breaking your customer base into groups that have similar characteristics, interests, values or spending habits. Segmenting them helps in understanding their needs and how your products or services provide value to them. Different segments may have different value propositions. We highly recommend creating customer personas for each of your customer segments.
Questions to ask yourself when defining your customer segment:
Who are we solving problems for?
Who values my value proposition?
Are they individuals or businesses?
What are the characteristics of those segments?
How can you make your segments more specific?
Customer Relationships
Determine the type of relationship you want to establish with each customer segment. It could range from personal assistance to automated services, depending on what's most appropriate for your product and customers. How will customers interact with your business as part of operations?
Channels
Channels are the avenues through which you reach your customer segments to deliver your value proposition. This includes marketing and sales channels, both online and offline.
Questions to ask yourself when defining your channel:
How are we going to tell our customer personas about our value proposition?
Where are our customers and how do they consume information? Conferences, social media, mail, TV, etc.
Key Activities
What crucial activities do your value proposition, channels, customer relationships, and revenue streams require? This could involve production, problem-solving, or platform/network maintenance.
Questions to ask yourself when defining your key activities:
What activities need to happen for you to deliver your value proposition to customers?
What different actions need to take place for your different service or product offerings?
Key Resources
Identify the most essential assets required to make your business model work. These can be physical, financial, intellectual, or human resources.
Key Partners
Some activities are outsourced, and some resources are acquired outside the enterprise. Key partners will include suppliers, distributors, or other strategic alliances. This should cover anything you need a third party to provide so that you can successfully deliver the value you promise to customers
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams define how your business earns money from each customer segment. Revenue streams can be generated through various means like direct sales, subscription fees, leasing, etc. This may be different for each customer segment or product offering.
Cost Structure
This outlines the major costs involved in operating your business model. Understanding the cost structure is vital for making your business model sustainable. Make sure you include everything that it takes to deliver your value proposition to your customer and don’t forget your overhead items. At the same time, this is designed to be high level so do not turn it into a financial forecast.
Now that you are armed with this knowledge, we hope that you can unlock the benefits of using the business model canvas to get that overview of your company or analyze an idea. If you need any help with this or making sure you are on a path to building abundance in your business, get in touch with us here.